The Studies of Antifungal Properties of Steroidal Saponin
Abstract
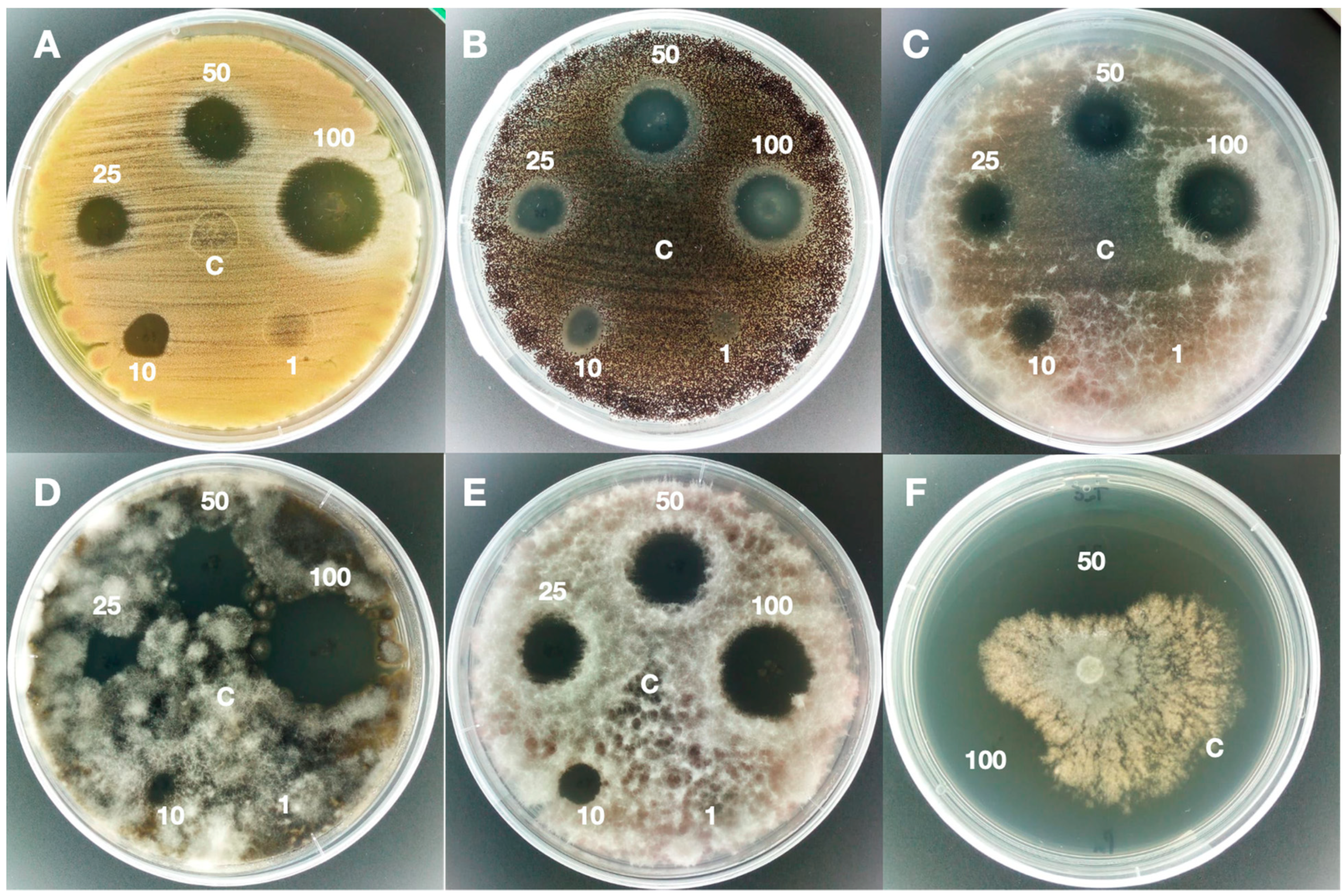
We examined the efficacy of 6 steroidal sapogenins and twenty-two saponins C-27 steroidal to stop the development of four prevalent opportunistic pathogens: Aspergillus species, Cryptococcus species, and Candidaspecies. It has been revealed that the effect of antifungus of steroidal saponins' is associated type of single saccharide. Out of a total of tensteroidal compounds, four compounds entity showed activity equivalent the positive control. The cytotoxicity of these substances against mammalian cells was distinct from their antifungusinfluence. The probable Carbon-27 steroidal saponins as antifungus show the way for preclinical investigation.
References
Bedir, E., I. A. Khan, and L. A. Walker.2002. Biologically active steroidal glycosides from Tribulus terrestris. Pharmazie57:491-493.
Borenfreund, E., and J. Puerner.1985. Toxicity determined in vitro morphological alterations and neutral red absorption. Toxicol. Lett.24:119-124.
Chen, H., Y. Xu, Y. Jiang, H. Wen, Y. Cao, W. Liu, and J. Zhang. July 2003. Application of Tribulus terrestris spirosteroidal saponin to prepare the antifungal medical preparations. Faming ZhuanliShenqingGongkaiShuomingshu. China patent 1428349.
De Lucca, A. J., J. M. Bland, C. B. Vigo, M. C. P. Selitrennikoff. October 2001. Fungicidal saponin, CAY-1, and isolation thereof from Capsicum species fruit. U.S. patent 6,310,091.
Dimoglo, A. S., I. N. Choban, I. B. Bersuker, P. K. Kintya, and N. N. Balashova.1985. Structure-activity correlations for the antioxidant and antifungal properties of steroid glycosides. Bioorg. Khim.11:408-413.
Feng, Z. Y.1994. Phase II clinical trial of Di-ao-xin-xue-kang in treating angina pectoris. New Drug Clin. Remed.13:152-155.
Imai, S., S. Fujioka, E. Murata, M. Goto, T. Kawasaki, and T. Yamauchi.1967. Bioassay of crude drugs and oriental crude drug preparations. XXII. Search for biologically active plant ingredients by means of antimicrobial tests. 4. Antifungal activity of dioscin and related compounds. Takeda Kenkyusho Nenpo26:76-83.
Jin, J. M., and C. R. Yang.2003. Two new spirostanol sapogenins from fermented leaves of Agave americana. Chin. Chem. Lett.14:491-494.
Jin, J. M., X. K. Liu, and C. R. Yang.2002. A new C-27 steroidal saponin from fermented leaves of Agave Americana. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi27:431-434.
Jin, J. M., X. K. Liu, and C. R. Yang.2002. New steroidal saponin from fermented leaves of Agave Americana. Acta Bot. Yunnanica24:539-542.
Jin, J. M., X. K. Liu, and C. R. Yang.2003. Three new hecogenin glycosides from fermented leaves of Agave americana. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res.5:95-103.
Jin, J. M., X. K. Liu, R. W. Teng, and C. R. Yang.2002. Two new steroidal glycosides from fermented leaves of Agave americana. Chin. Chem. Lett.13:629-632.
Jin, J. M., X. K. Liu, R. W. Teng, and C. R. Yang.2002. Enzymatic degradation of parvifloside. Acta Bot. Sin.44:1243-1249.
Jin, J. M., Y. J. Zhang, and C. R. Yang.2004. Four new steroid constituents from the waste residue of fiber separation from Agave americana leaves. Chem. Pharm. Bull.52:654-658.
Jin, J. M., Y. J. Zhang, and C. R. Yang.2004. Spirostanol and furostanol glycosides from the fresh tubers of Polianthes tuberosa. J. Nat. Prod.67:5-9.
Jin, J. M., Y. J. Zhang, H. Z. Li, and C. R. Yang.2004. Cytotoxic steroidal saponins from Polygonatumzanlanscianense. J. Nat. Prod.67:1992-1995.
Keating, G. M., and D. P. Figgitt.2003. Caspofungin: a review of its use in esophageal candidiasis, invasive candidiasis and invasive aspergillosis. Drugs63:2235-2263.
Li, B. G., and Z. Z. Zhou.1994. Chemistry of the new drug Di-ao-xin-xue-kang treating angina pectoris. New Drug Clin. Remed.13:75-76.
Li, T. K., R. Zhou, S. H. Zhao, and L. G. Hu.2000. Clinical studies on Zu-shi-ma injection. New Trad. Chin. Med. Clin. Pharmacol.11:266-268.
Liang, B. B., and R. Wang.2004. The adverse reaction and advances in study on antifungal drugs. Clin. Med. J.2:5-12.
Liu, W. D., and C. H. Lian.2003. The early stage diagnosis of deep-seated fungal infections. Chin. J. Lab. Med.26:583-584.
Magota, H., K. Okubo, M. Shimoyamada, M. Suzuki, and M. Maruyama.March 1991. Isolation of steroidal saponin as antifungal agent. Japan patent 03048694.
Marr, K. A., C. N. Lyons, K. Ha, T. Rustad, and T. C. White.2001. Inducible azole resistance associated with a heterogeneous phenotype in Candida albicans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.45:52-59.
Marr, K. A., C. N. Lyons, T. Rustad, R. A. Bowden, and T. C. White.1998. Rapid, transient fluconzole resistance in Candida albicans is associated with increased mRNA levels of CDR. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.42:2584-2589.
NCCLS.2002. Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of yeasts; approved standard M27-A2. National Committee on Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne, Pa.
NCCLS.2002. Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of filamentous fungi; approved standard, M38-A. National Committee on Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne, Pa.
Ren, L. J.2004. The clinical application of common antifungal drugs. China New Med.3:63-64.
Saito, S., and Y. Nagamura.March 1996. Therapeutic agents for hepatitis. Japan patent 8059476.
Sashida, Y., Y. Mitsumaki, A. Kuroda, T. Takashi, and K. Sudo.July 2001. Antifungal steroid saponin. Japan patent 2001181296.
Sautour, M., A.-C. Mitaine-Offer, T. Miyamoto, A. Dongmo, and M.-A. Lacaille-Dubois.2004. Antifungal steroid saponins from Dioscoreacayenensis. Planta Med.70:90-92.
Sparg, S. G., M. E. Light, and J. V. Staden.2004. Biological activities and distribution of plant saponins. J. Ethnopharmacol.94:219-243.
Singh Ramgopal,. Seth Rupsa. 2021. Discussing Current Knowledge On Saponins: Structure, Sources And Cytoxicity. Drugs and Cell Therapies in Hematology, 10(3), 229–233.
Ahmad FerozShergojri, Saxena Akanksha Anand. (2021). Studying Design Structure And Categories Of Antimicrobial Peptides (Amps). Drugs and Cell Therapies in Hematology, 10(3), 312–317.
Upadhyay Akash, Shalini Suchita. (2021). Significance Of Secondary Prevention Of Cardiovascular Diseases And Related Lifestyle Intervention. Drugs and Cell Therapies in Hematology, 10(3), 263–267.